most tasks are executed very fast, but some tasks are extremely slow.
1. Spark Data Skew
For example, there are a total of 1,000 tasks, 997 tasks are executed within 1 minute, but the remaining two or three tasks take one or two hours. This situation is very common.
Most tasks are executed very fast, but some tasks are extremely slow.
the progress of the entire Spark job is determined by the task with the longest running time.
2. The principle of Data Skew
when performing shuffle, the same key on each node must be pulled to a task on a node for processing, such as aggregation or join operations according to the key.
For example, most keys correspond to 10 pieces of data, but individual keys correspond to 1 million pieces of data, so most tasks may only be assigned to 10 pieces of data, and then run out in 1 second; but individual tasks may be assigned 1 million pieces The data will run for one or two hours.
| No. | trigger shuffle operations when data skew, it may be caused by using one of these operators. |
|---|---|
| 1. | distinct |
| 2. | groupByKey |
| 3. | reduceByKey |
| 4. | aggregateByKey |
| 5. | join, cogroup, repartition, etc. |
3. The execution of a task slow
The first thing to look at is which stage of data skew occurs in.
- yarn-client submit, you can see the log locally, find which stage is currently running in the log;
- yarn-cluster submit, Spark Web UI Run to the first few stages.
Whether using the yarn-client mode or the yarn-cluster mode, we can take a deep look at the amount of data allocated by each task of this stage on the Spark Web UI, so as to further determine whether the uneven data allocated by the task causes data skew.
After knowing which stage the data skew occurs, then we need to calculate which part of the code corresponds to the stage where the skew occurs based on the principle of stage division.
solution: as long as you see a shuffle operator or Spark SQL SQL in the Spark code If there is a statement that will cause shuffle in the statement (such as a group by statement), then it can be determined that the front and the back stage are divided by that place.
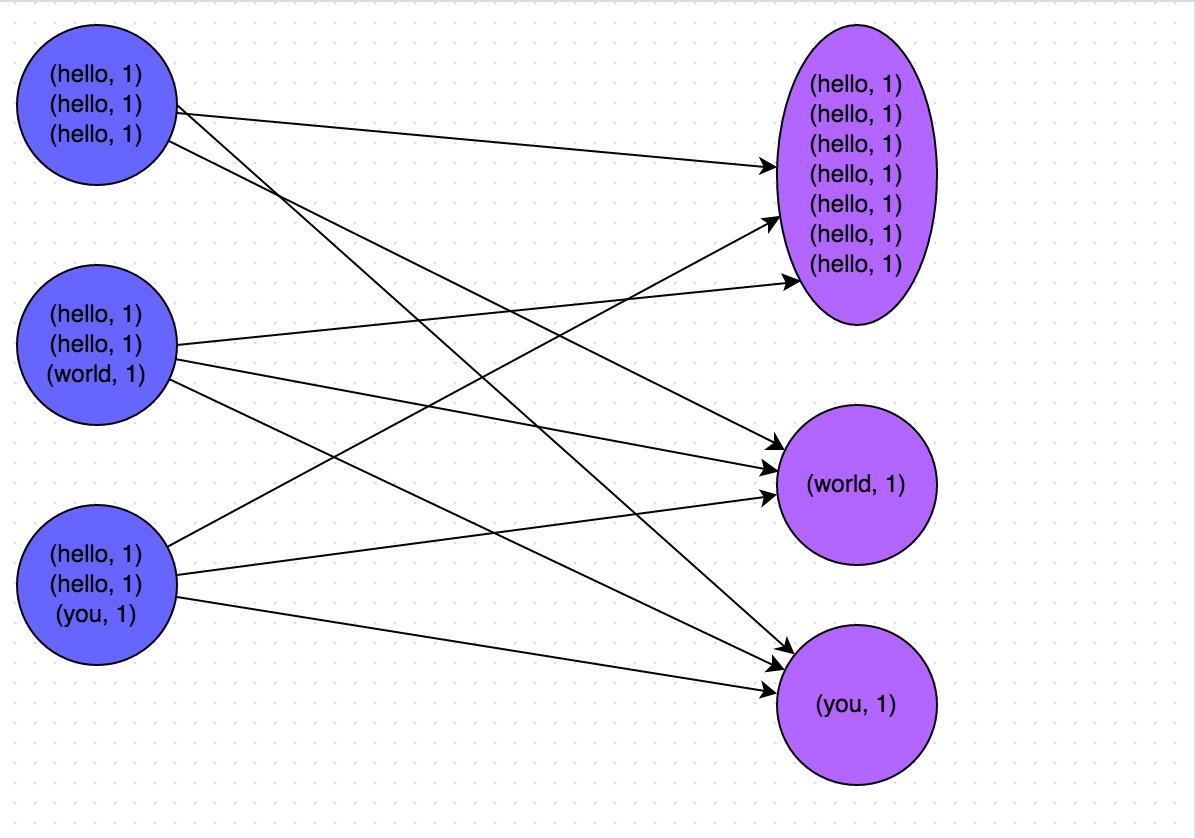
Word Count
1 | val conf = new SparkConf() |
3.1 stages divided
the entire code, only one reduceByKey operator will shuffle, the front and back stages will be divided.
* stage0, mainly to perform operations from textFile to map, and perform shuffle write operations.
3.2 shuffle write
The shuffle write operation can be simply understood as partitioning the data in the pairs RDD. In the data processed by each task, the same key will be written to the same disk file.
* Stage1 is mainly to perform operations from reduceByKey to collect.
3.3 shuffle read
When each task of stage1 starts to run, it will first perform shuffle read operation. The task that performs the shuffle read operation will pull those keys that belong to the node where each task of stage 0 is located, and then perform operations such as global aggregation or join on the same key. Here, the value of the key is accumulated.
After stage1 executes the reduceByKey operator, it calculates the final wordCounts RDD, and then executes the collect operator to pull all the data to the Driver for us to traverse and print out.
4. data skew - distribution of keys
| No. | View the data distribution of keys that cause data skew |
|---|---|
| 1. | If the data skew caused by the group by and join statements in Spark SQL, then query the key distribution of the table used in SQL Happening. |
| 2. | If the data skew is caused by the shuffle operator on Spark RDD, you can view the key distribution in the Spark job, such as RDD.countByKey(). Then, collect/take, see the distribution of the keys. |
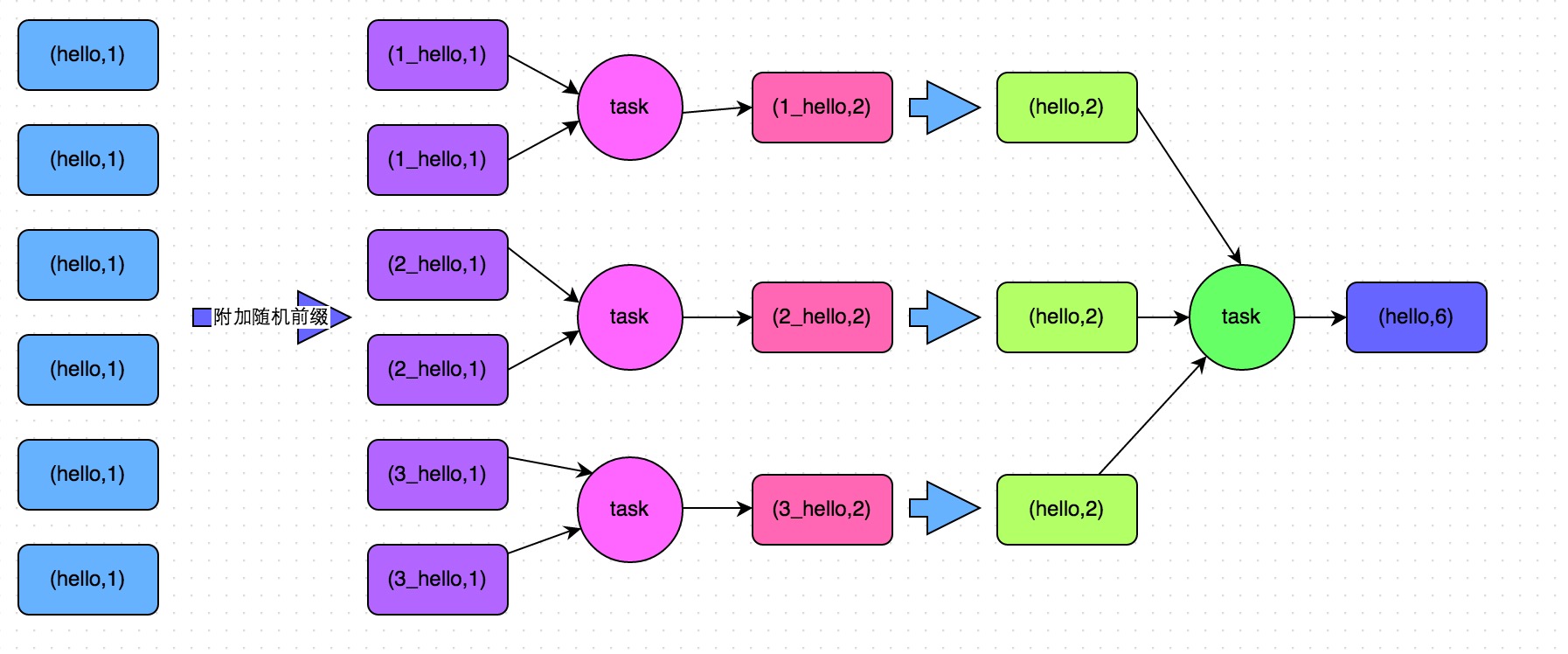
For example, Word Count
we can first sample 10% of the sample data for pairs, then use the countByKey operator to count the number of occurrences of each key, and finally traverse and print the number of occurrences of each key in the sample data on the client.
1 | val sampledPairs = pairs.sample(false, 0.1) |
| No. | solutions of the data skew |
|---|---|
| 1. | Improve the parallelism of shuffle operations 在对RDD执行shuffle算子时,给shuffle算子传入一个参数,比如reduceByKey(1000),该参数就设置了这个shuffle算子执行时shuffle read task的数量 Spark SQL中的shuffle类语句,比如group by、join等,需要设置一个参数,即spark.sql.shuffle.partitions,该参数代表了shuffle read task的并行度,该值默认是200,对于很多场景来说都有点过小。 Experience: cannot completely solve the data skew,such as the amount of data a key is 1 million. |
| 2. | Two-stage aggregation (local aggregation + global aggregation) disadvantages: only solve aggregate shuffle operations. If it is a shuffle operation of the join class, other solutions have to be used. |
| 3. | Convert reduce join to map join advantages: The effect is very good for data skew caused by the join operation, because shuffle and data skew will not happen at all. disadvantages: only suitable for a large table and a small table. After all, we need to broadcast the small table, which consumes more memory resources. The driver and each Executor will have a full amount of data of a small RDD in the memory. If the RDD data we broadcast is relatively large, such as 10G or more, then memory overflow may occur. Therefore, it is not suitable for the situation where both are large tables. |
1 | import sys |
WordCounts reduceByKey More Info...
1 | # read data from text file and split each line into words |
1 | # count the occurrence of each word |
[('0_Singapore', 3),
('2_bbb', 1),
('0_hello', 1),
('2_haha', 1),
('0_world', 1),
('1_ShangHai', 1),
('0_China', 1),
('2_Singapore', 4),
('1_Singapore', 1),
('2_hello', 1)]
1 | words_recover = wordCounts.map(lambda x: (x[0][x[0].find('_')+1:], x[1])) |
[('world', 1), ('ShangHai', 1), ('China', 1), ('Singapore', 8), ('bbb', 1)]
5. Convert reduce join to map join
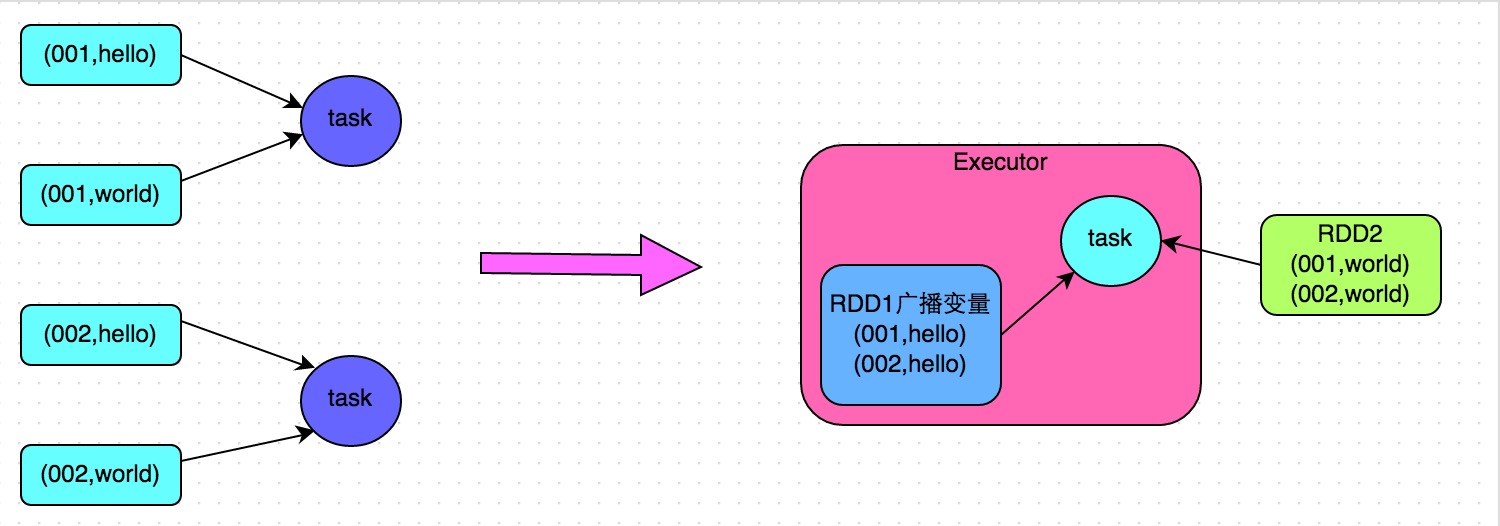
code:
1 | // 首先将数据量比较小的RDD的数据,collect到Driver中来。 |
方案实践经验:曾经开发一个数据需求的时候,发现一个join导致了数据倾斜。优化之前,作业的执行时间大约是60分钟左右;使用该方案优化之后,执行时间缩短到10分钟左右,性能提升了6倍。
Other Solution 1: Use Hive ETL to preprocess data
Other Solution 2: Filter a few keys that cause skew
Reference
- https://github.com/wwcom614/Spark/blob/master/src/main/scala/com/ww/rdd/performance_optimize/BroadcastMapJoins.scala
- 每个Spark工程师都应该知道的
- Spark的五种JOIN策略解析
- SparkSQL中的三种Join及其具体实现(broadcast join、shuffle hash join和sort merge join
- Spark Join——Broadcast Join、Shuffle Hash Join、Sort Merge Join
- spark sql优化:小表大表关联优化 & union替换or & broadcast join
- Hive数仓建表该选用ORC还是Parquet,压缩选LZO还是Snappy?
- Spark实践 – 性能优化基础
- 尚硅谷2021迎新版大数据Spark从入门到精通
- 尚硅谷大数据电商数仓V3.0版本教程(数据仓库项目开发实战)
- Spark Sql 与 MySql 使用 group by 的差别






Checking if Disqus is accessible...