1.1 二分查找, while l <= r
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution : def search (self, nums: List [int ], target: int ) -> int : if not nums: return -1 l, r = 0 , len (nums) - 1 while l <= r: mid = (r - l)//2 + l if nums[mid] < target: l = mid + 1 elif nums[mid] > target: r = mid - 1 else : return mid return -1
34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution : def searchRange (self, nums: List [int ], target: int ) -> List [int ]: if not nums: return [-1 , -1 ] def binSearch (nums, t, flag ): l, r = 0 , len (nums) - 1 while l <= r: mid = (l + r) // 2 if nums[mid] > t: r = mid - 1 elif nums[mid] < t: l = mid + 1 else : if flag == "L" : r = mid - 1 else : l = mid + 1 if flag == 'L' and r + 1 < len (nums) and nums[r + 1 ] == t: return r + 1 if flag == 'R' and l - 1 >= 0 and nums[l - 1 ] == t: return l - 1 return -1 return [binSearch(nums=nums, t=target, flag='L' ), binSearch(nums=nums, t=target, flag='R' )]
88. 合并两个有序数组 - 逆向双指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from typing import List class Solution : def merge (self, A: List [int ], m: int , B: List [int ], n: int ) -> None : """ Do not return anything, modify A in-place instead. """ pa, pb = m - 1 , n - 1 tail = m + n - 1 while pa >= 0 or pb >= 0 : if pa == -1 : A[tail] = B[pb] pb -= 1 elif pb == -1 : A[tail] = A[pa] pa -= 1 elif A[pa] > B[pb]: A[tail] = A[pa] pa -= 1 else : A[tail] = B[pb] pb -= 1 tail -= 1 return A[:]
15. 3Sum - for for while , second_ix & third_ix 两边夹
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution : def threeSum (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [List [int ]]: n = len (nums) nums.sort() ans = list () for first in range (n): if first > 0 and nums[first] == nums[first - 1 ]: continue third = n - 1 target = -nums[first] for second in range (first + 1 , n): if second > first + 1 and nums[second] == nums[second - 1 ]: continue while second < third and nums[second] + nums[third] > target: third -= 1 if second == third: break if nums[second] + nums[third] == target: ans.append([nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]]) return ans
11. Container With Most Water 双指针 - 移动 l 和 r 较小的一方才可能增加 area
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def maxArea (self, height: List [int ] ) -> int : l, r = 0 , len (height) - 1 area = 0 while l < r: area = max (area, min (height[l], height[r]) * (r-l)) if height[l] < height[r]: l += 1 else : r -= 1 return area
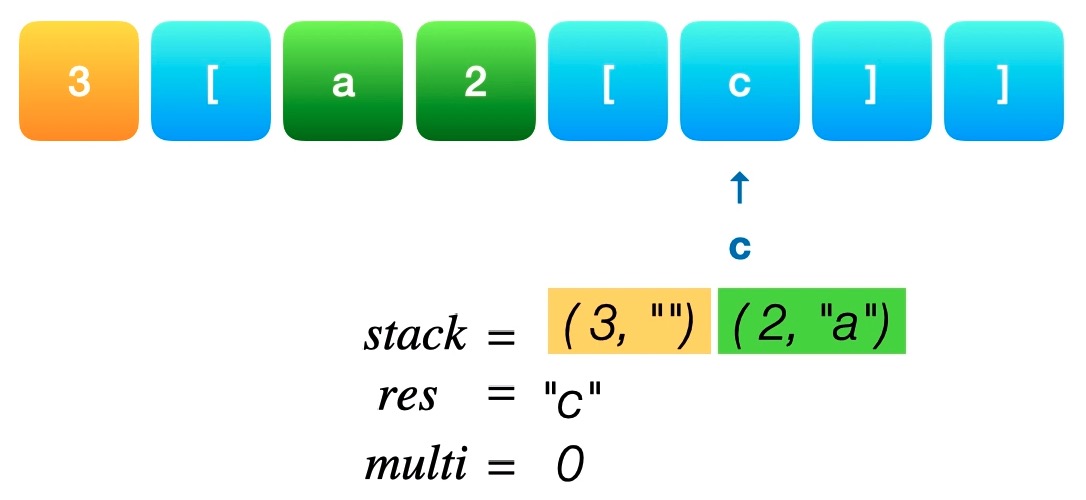
2.1 字符串解码 “3[a2[c]]” == “accacc” , stack == [(3, ""), (2,"a")]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution : def decodeString (self, s: str ) -> str : stack, res, multi = [], "" , 0 for c in s: if c == '[' : stack.append([multi, res]) res, multi = "" , 0 elif c == ']' : cur_multi, last_res = stack.pop() res = last_res + cur_multi * res elif '0' <= c <= '9' : multi = multi * 10 + int (c) else : res += c return res
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 from heapq import heapify, heappush, heappop class Solution : def findKthLargest (self, nums: List [int ], k: int ) -> int : n = len (nums) if k == 0 or k > n: return [] hp = nums[:k] heapify(hp) for i in range (k, n): v = nums[i] if v > hp[0 ]: heappop(hp) heappush(hp, v) return hp[0 ]
Using dynamic programming to solve problems is generally 3 steps:
state
Find the state transition equation
Boundary processing
When analyzing the state of the problem, don’t analyze the whole, just analyze the last stage! Because dynamic programming problems are divided into multiple stages, the state representation of each stage is the same, and our final answer is in the last stage.
爬楼梯 climbing-stairs , ✔️ 新建{}or[] ,滚动数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution : def climbStairs (self, n: int ) -> int : dp = {} dp[1 ] = 1 dp[2 ] = 2 for i in range (3 ,n+1 ): dp[i] = dp[i-1 ] + dp[i-2 ] return dp[n]
No.
dynamic programming
Flag
no-gd
31. n个骰子的点数 dp[i][j] ,表示投掷完 i 枚骰子后,点数 j 的出现次数✔️
Summary 20 dynamic programming
(4.1)
DP表示状态
easy
Climbing Stairs , 新建{}or[] ,滚动数组 ❎
addition
63. 多少种 不同路径 II , store = [[0]*n for i in range(m)] 二维初始化❎
Edit Distance/编辑距离 【word1 转换成 word2】
addition
5. Longest Palindromic Substring/最长回文子串 ✔️❎
good
把数字翻译成字符串 Fib ✔️❎
addition
Leetcode 64. Minimum Path Sum, 最小路径和 grid[i][j] = min(grid[i - 1][j], grid[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j]
❎
addition
115. Distinct Subsequences I
Hard
addition
940. 不同的子序列 II
Hard
addition
Interleaving String/交错字符串
Hard
No.
Question
Flag
(6).
sliding Window
65. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串 滑动窗口
✔️❎
14. 和为s的连续正数序列 [sliding window]
✔️❎
(7).
模拟
21. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字 东大 Lucien 题解,讲得最清楚的那个。官方讲解有误
35. 顺时针打印矩阵 left, right, top, bottom = 0, columns - 1, 0, rows - 1
✔️❎
56. 把数组排成最小的数, sorted vs sort, strs.sort(key=cmp_to_key(sort_rule))
✔️❎
70. 把字符串转换成整数 31-1, -2 31, 2**31//10
✔️❎
No.
Question
Flag
(3).
linkedList
7. 从尾到头打印链表: reversePrint(head.next) + [head.val]
❎
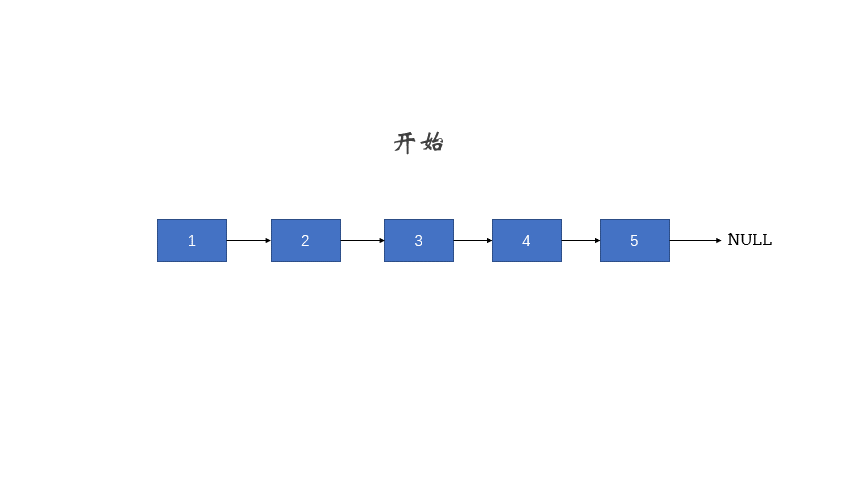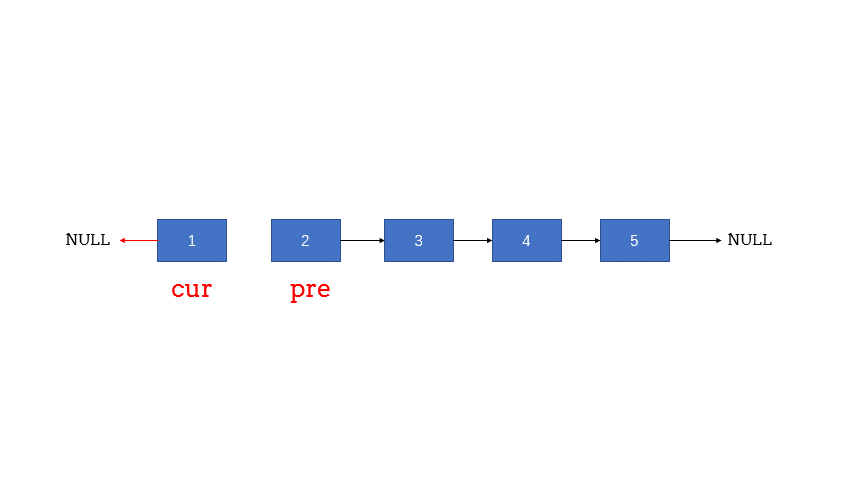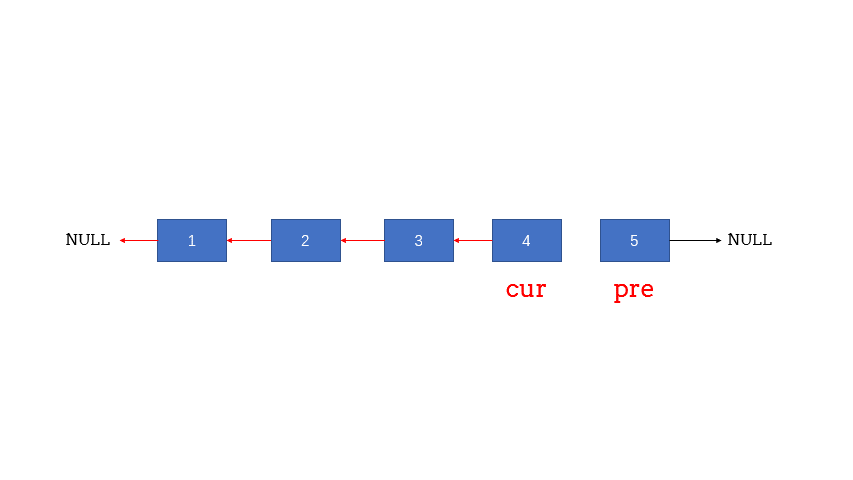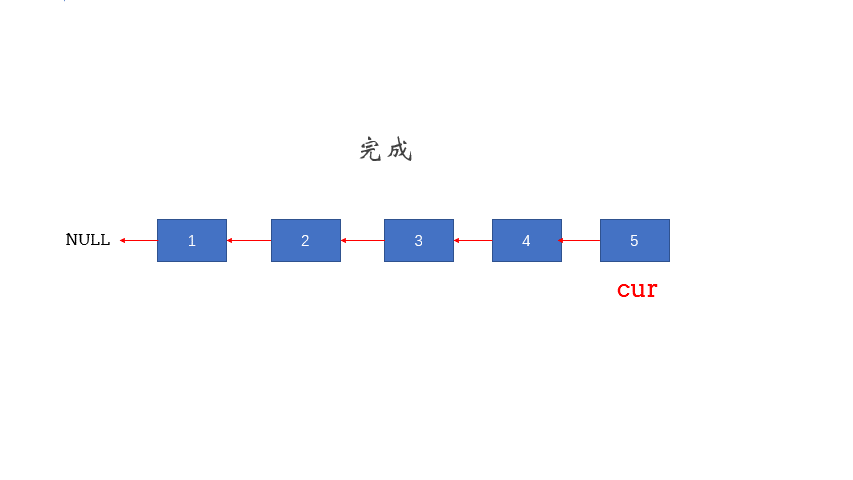
8. 反转链表 pre, cur = head, head.next pre.next = None (循环版 双指针)
❎
10. 合并两个排序的链表 [Recursion ]
❎
addition
旋转单链表 (F1. 环 F2. 走n-k%n 断开)
❎
addition
92. 翻转部分单链表 reverse(head: ListNode, tail: ListNode) ❎
addition
链表划分, 描述: 给定一个单链表和数值x,划分链表使得小于x的节点排在大于等于x的节点之前
❎
addition
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II 链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5.❎
addition
输入:(7 -> 1 -> 6) + (5 -> 9 -> 2),即617 + 295
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class ListNode : def __init__ (self, val=0 , next =None ): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution : def reversePrint (self, head: ListNode ) -> List [int ]: if head is None : return [] else : return self.reversePrint(head.next ) + [head.val] head = ListNode(1 ) head.next = ListNode(3 ) head.next .next = ListNode(2 ) solution = Solution() result = solution.reversePrint(head) print (result)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class ListNode : def __init__ (self, x ): self.val = x self.next = None class Solution (object def reverseList (self, head ) -> ListNode: if not head or not head.next : return head pre, cur = head, head.next pre.next = None while cur: tmp = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = tmp return pre
合并2个有序链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution : def mergeTwoLists (self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode ) -> ListNode: if l1 is None : return l2 if l2 is None : return l1 if l1.val < l2.val: p = ListNode(l1.val) p.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next , l2) else : p = ListNode(l2.val) p.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next ) return p
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class ListNode : def __init__ (self, val=0 , next =None ): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution : def rotateRight (self, head: ListNode, k: int ) -> ListNode: if not head or not head.next or k == 0 : return head length = 1 tail = head while tail.next : tail = tail.next length += 1 tail.next = head new_tail_pos = length - k % length - 1 new_tail = head for _ in range (new_tail_pos): new_tail = new_tail.next new_head = new_tail.next new_tail.next = None return new_head head = ListNode(1 ) head.next = ListNode(2 ) head.next .next = ListNode(3 ) head.next .next .next = ListNode(4 ) head.next .next .next .next = ListNode(5 ) head.next .next .next .next .next = ListNode(6 ) solution = Solution() k = 3 new_head = solution.rotateRight(head, k) current = new_head while current: print (current.val, end=" -> " if current.next else " -> NULL" ) current = current.next
No.
Question
Flag
(2).
Stack
394. 字符串解码 [a]2[bc] ❎
28. 包含min函数的栈 ❎
29. 最小的k个数【堆排的逆向】 heapq.heappop(hp),heapq.heappush(hp, -arr[i])✔️❎
36. 滑动窗口的最大值 (同理于包含 min 函数的栈) deque.popleft(),双端队列+单调
✔️❎
59 II. 队列的最大值 , 维护个单调的deque ✔️❎
(5).
DFS / BFS
66. 矩阵中的路径 , 经典好题: 深搜+回溯 def dfs(i, j, k):✔️❎
61. 机器人的运动范围 bfs good from queue import Queue, q.get() q.pup()✔️❎
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from collections import dequeclass Solution : def movingCount (self, m: int , n: int , k: int ) -> int : q = deque() q.append((0 ,0 )) s = set () s.add((0 ,0 )) while q: x, y = q.popleft() for (i, j) in [(x+1 , y), (x, y+1 )]: if valid(i, j, k, s, m, n): q.append((i, j)) s.add((i, j)) return len (s)
剑指
No.
Question
Flag
easy
(1).
Tree
1.1 平衡二叉树 ❎
1.2 对称的二叉树 ❎
1.3 二叉树的镜像 : 递归+swap后 ❎
1.4 二叉搜索树的第k大节点 [中序遍历 倒序, 右-中-左]✔️❎
good
1.5 (两个节点)二叉树的最近公共祖先 [Recursion ] 后序遍历+路径回溯✔️❎
good
1.6 (两个节点)二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 Recursion + 剪枝✔️❎
good
1.7 二叉树中和为某一值的路径 递归回溯✔❎️
1.8 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 ❎
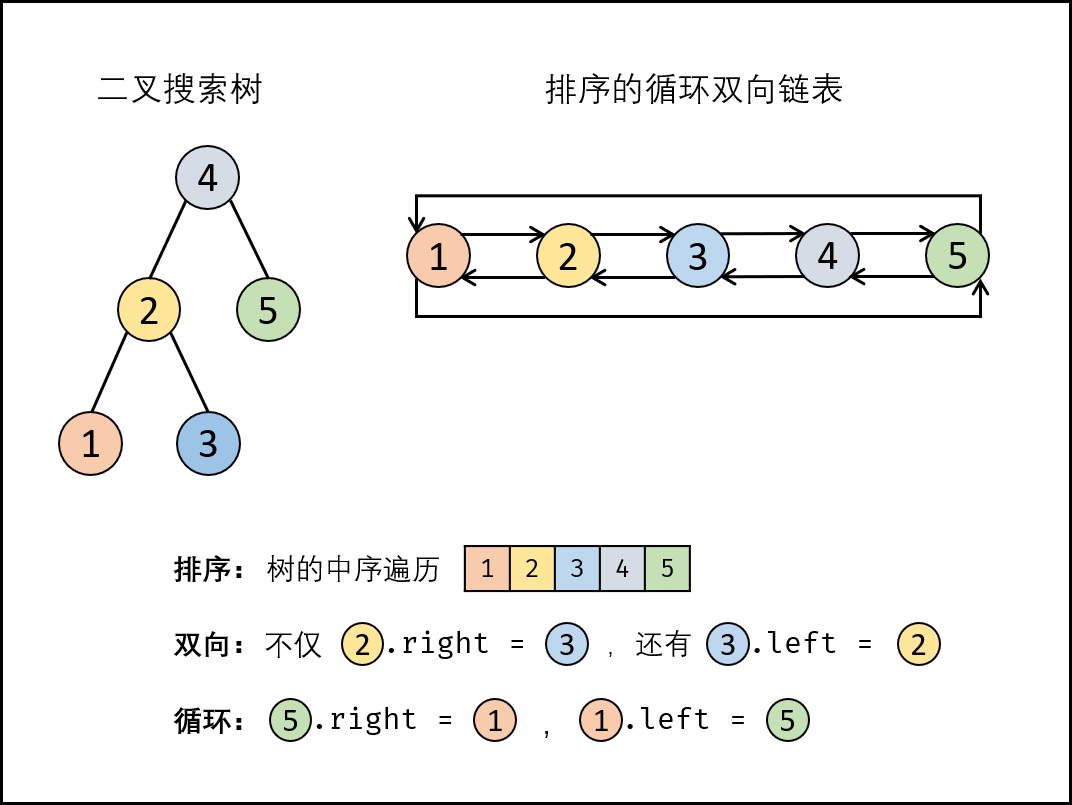
1.9 二叉搜索树与双向链表
additional
求二叉树第K层的节点个数 [Recursion ] ,root != None and k==1,返回1
❎
additional
求二叉树第K层的叶子节点个数 [Recursion ]
✔️❎
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class TreeNode : def __init__ (self, x ): self.val = x self.left = None self.right = None class Solution : def isBalanced (self, root: TreeNode ) -> bool : def maxHigh (root ): if root == None : return 0 return max (maxHigh(root.left), maxHigh(root.right)) + 1 if root == None : return True return abs (maxHigh(root.left) - maxHigh(root.right)) <= 1 and self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)







Checking if Disqus is accessible...